Solving the Complexity of Utility Metering Standards
Utility metering relies on a highly specialized set of communication standards designed to ensure accurate data transmission for electricity, water, gas, and heat consumption. These protocols, such as M-Bus (Meter-Bus), Wireless M-Bus, DLMS/COSEM, and specialized variants of Modbus, are often complex and rigorously defined. Unlike more common consumer protocols, documentation for these standards can be scarce, and valid implementation requires deep domain expertise. This category provides hardware solutions that bridge the gap between general-purpose microcontrollers and these demanding metering networks, ensuring compliance and reliability without the need for extensive research into obscure technical specifications.
Accelerating Market Entry for Smart Metering Solutions
The development of interfaces for utility meters is frequently hindered by the steep learning curve associated with their proprietary or restricted protocols. INACKS integrated circuits and modules help a lot to develop products with this category because it avoids the firmware engineer to have to implement by itself the protocol, therefore there are less costs, and product can be ended sooner. By offloading the protocol management to our dedicated chips, businesses can bypass the months of coding and testing typically required to build a compliant stack. This allows your engineering team to focus entirely on the core business logic and value proposition of the product, rather than getting lost in the intricacies of data transport layers.
Top 10 Utility Meter Protocols & Standards
Our components support the most critical protocols used in the global metering industry, ensuring interoperability across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
M-Bus (Meter-Bus): The European standard for reliable remote reading of heat, water, and gas meters.
Wireless M-Bus: The wireless variant of M-Bus (EN 13757-4), widely used for flexible, low-power meter data collection.
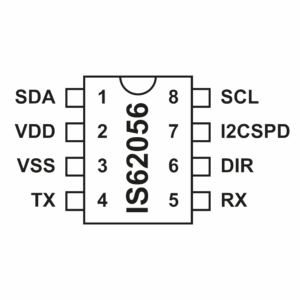
DLMS/COSEM (IEC 62056): The global standard for energy metering data exchange, ensuring semantic interoperability for smart electricity meters.
EN 13757-2 / EN 13757-3: The physical and link layers (part 2) and application layers (part 3) that form the backbone of M-Bus communication.
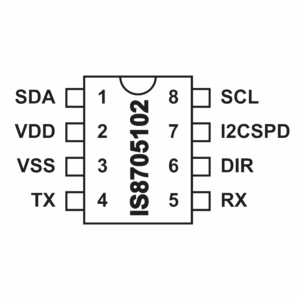
IEC 870-5-102: A companion standard for the transmission of integrated totals in electric power systems, frequently utilized in specific European grid markets.
OpenHAN: An open standard for Home Area Networks, connecting utility meters with in-home displays and energy management devices.
PRIME (PoweRline Intelligent Metering Evolution): A mature Power Line Communication (PLC) standard used for smart grid data transmission over existing electrical wiring.
Modbus RTU/TCP: A ubiquitous industrial protocol often used to integrate energy meters into Building Management Systems (BMS) and SCADA.
LoRaWAN: A long-range, low-power protocol increasingly adopted for water and gas metering in geographically dispersed areas.
Zigbee Smart Energy: A wireless standard specifically designed to monitor, control, and automate the delivery and use of energy and water.
Check Other Categories
Industrial Protocols | Lighting Protocols | Image/Video | Storage | USB Peripheral | IoT Protocols | Utility Meter